3500 million years to today
![]()
Geological era: Archean
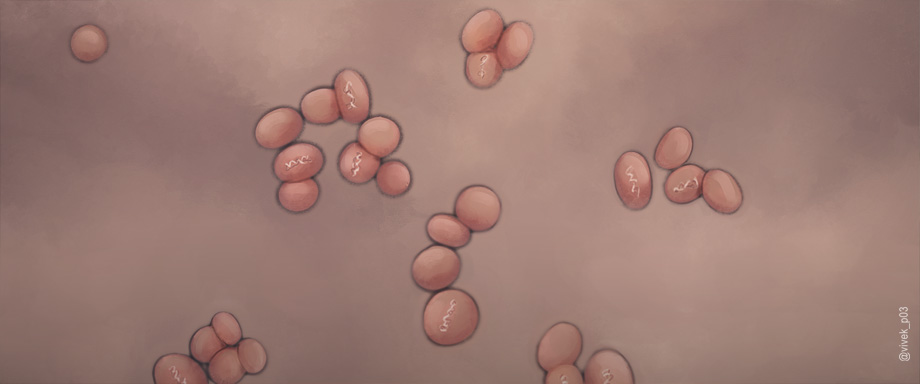 Precursors of cyanobacteria (formerly called blue-green algae) are the first cells whose traces can be detected in old rocks. Thanks to their cell membrane they were able to regulate the exchange of substances and energy with their environment.
Precursors of cyanobacteria (formerly called blue-green algae) are the first cells whose traces can be detected in old rocks. Thanks to their cell membrane they were able to regulate the exchange of substances and energy with their environment.
Limestone precipitations (stromatolites) of other microorganisms are also detectable from this period.
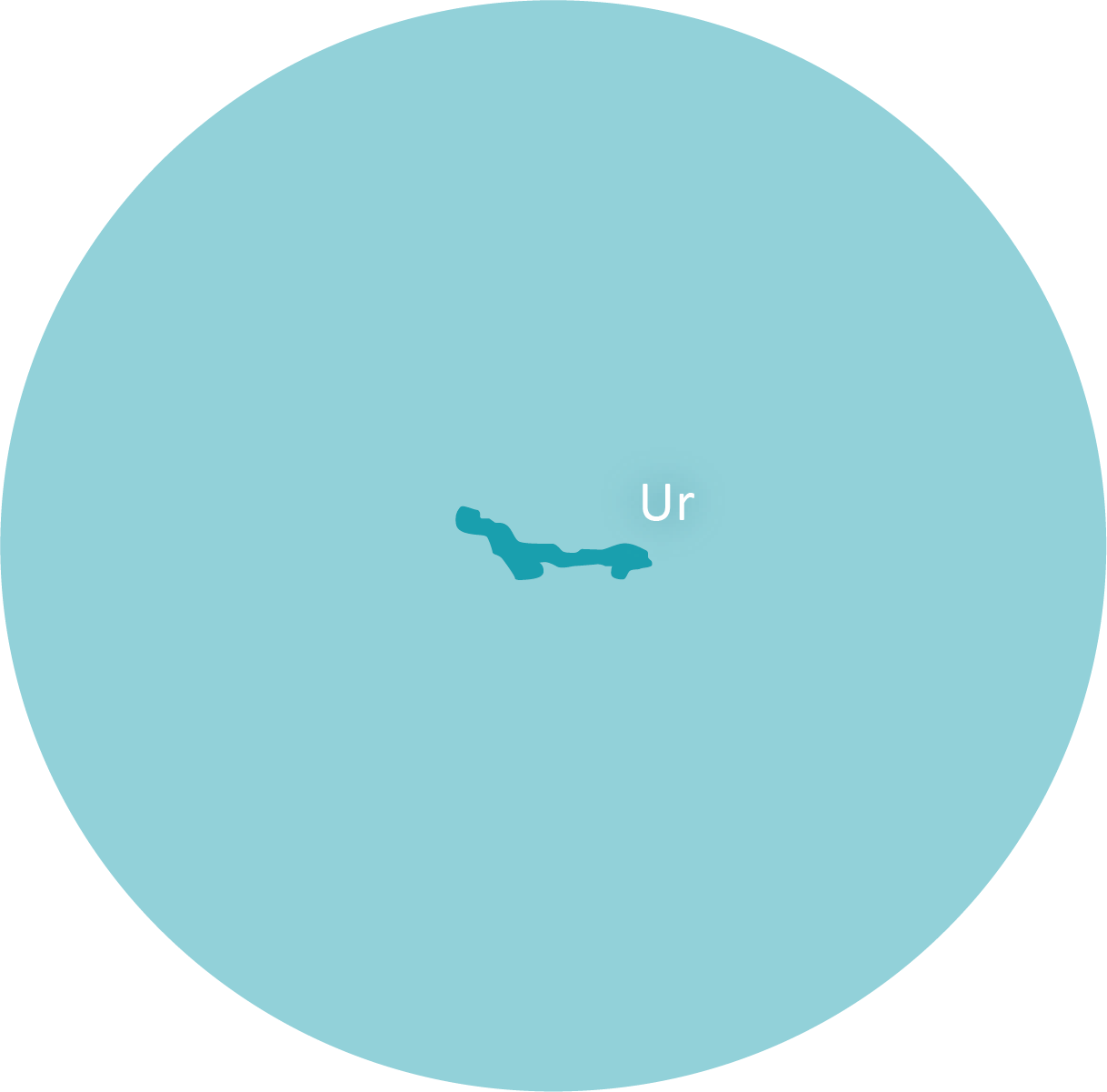
The carbon dioxide originally present in the atmosphere dissolves in the oceans and is used there to build up biomass. As a result, the atmosphere now consists almost entirely of nitrogen. Oxygen is not yet present, and accordingly there is no ozone layer that protects against UV rays. During this period the supercontinent Ur might have formed.







